Foothill Yellow Legged Frog
The foothill yellow-legged frog has a mottled body and it can release chemicals to protect itself from predators. The frog does not have a specific breeding season, as it can postpone mating if conditions are not conducive.
| Kingdom | Animalia |
| Phylum | Chordata |
| Class | Amphibia |
| Order | Anura |
| Family | Ranidae |
| Genus | Rana |
| Scientific Name | Rana boylii |
| Size | 1.45-3.23 in (3.6 -8.2 cm) |
| Color | Green or grayish body, sometimes red, adults have yellow legs |
| Call | Faint voice |
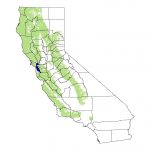
| Distribution | Oregon and California of the United States of America |
| Habitat | Rivers or flowing streams with rocky base |
| Diet | Tadpoles eat algae while adults prefer moths, hornets, snails, ants, grasshoppers, flies, water striders, and beetles |
| Predators | Western toads, bullfrogs, rough-skinned newts, garter snakes, water bugs, and diving beetles |
| Breeding Age | Around 6 months |
| Mode of Reproduction | Oviparous |
| Clutch Size | 100-1,000 eggs |
| Average Lifespan | Not known |
| IUCN Conservation Status | Near Threatened |
Foothill Yellow Legged Frog Pictures Gallery
- Foothill Yellow Legged Frog Eggs
- Foothill Yellow Legged Frog Images
- Foothill Yellow Legged Frog Photos
- Foothill Yellow Legged Frog Pictures
- Foothill Yellow Legged Frog Range
- Foothill Yellow Legged Frog Tadpole
- Foothill Yellow Legged Frog
- Rana boylii
Published on September 17th 2019 by staff under Frogs. Article was last reviewed on 14th September 2019.